The McKinsey Three Horizons Model is a strategic framework that helps organizations manage their growth and innovation over different time frames. It provides a structured way to think about the present and future potential of a business, ensuring a balanced approach to strategy development. This article will delve into the intricacies of the model, its benefits, challenges, and practical strategies for implementation.
Introduction to the McKinsey Three Horizons Model
The McKinsey Three Horizons Model was developed by the consulting firm McKinsey & Company to assist businesses in visualizing their strategic focus over varying time periods. It distinguishes three different horizons that represent different stages of opportunity and resource allocation.
This model encourages companies to look beyond immediate business concerns and to consider growth opportunities that may not yet be fully realized. By analyzing the three horizons, organizations can align their operations with long-term strategic goals, ensuring sustained performance.
The Concept Behind the Model
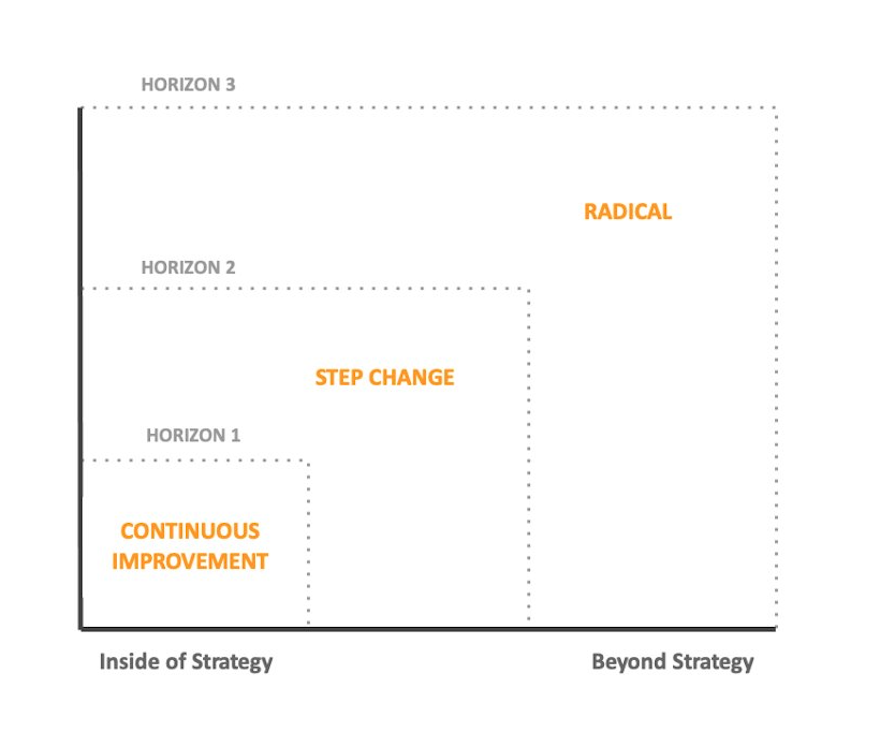
At its core, the Three Horizons Model separates an organization’s activities into three categories: the core business, emerging opportunities, and long-term possibilities. Each horizon addresses distinct time frames for strategic planning:
- Horizon 1: Focuses on the existing core business, optimizing performance and dealing with current challenges.
- Horizon 2: Emphasizes a set of emerging opportunities that can be developed into profitable initiatives.
- Horizon 3: Looks far ahead to long-term opportunities that may not yet be clear or developed, requiring visionary thinking.
The Importance of Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is crucial for any organization seeking to thrive amidst changing market conditions. The McKinsey Three Horizons Model supports this by encouraging businesses to maintain a balance between short-term objectives and long-term aspirations.
By utilizing this model, organizations can not only react to immediate market needs but also proactively invest in future growth areas, ensuring they remain competitive in the long run. Additionally, the model fosters a culture of innovation by prompting teams to explore new ideas and technologies that could disrupt the current market landscape. This forward-thinking approach can lead to breakthroughs that significantly enhance a company's value proposition and market share.
Moreover, the Three Horizons Model serves as a communication tool within organizations, helping stakeholders understand the rationale behind strategic decisions. By clearly delineating the focus areas across the three horizons, companies can better engage employees, investors, and partners in their vision for growth. This transparency can enhance collaboration and alignment across departments, driving a unified effort toward achieving both immediate results and future ambitions.
Detailed Overview of the Three Horizons
Understanding the specific characteristics and purposes of each horizon is essential for effectively implementing the McKinsey model. This section explores Horizons 1, 2, and 3 in greater detail, highlighting their significance in the overall strategic framework.
Horizon 1: Core Business
Horizon 1 is centered on a company's existing products and services. It involves maximizing revenue from the core business by improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reducing costs. Organizations should focus on:
- Strengthening their market position
- Increasing profitability through existing offerings
- Addressing any imminent challenges that may impact current operations
A robust focus on Horizon 1 is essential to generate the cash flow necessary for funding initiatives in other horizons. This horizon requires a meticulous analysis of customer feedback and market trends to ensure that the company remains competitive. By leveraging data analytics, businesses can identify areas for improvement in their product lines and customer service, thereby fostering loyalty and repeat business. Additionally, investing in employee training and development can enhance productivity and innovation within existing teams, leading to a more agile organization that can respond swiftly to market demands.
Horizon 2: Emerging Opportunities
Horizon 2 is where innovation begins to take center stage. Companies investigate new markets, technologies, and business models that could enhance their existing offerings or create new ones. Key activities in this horizon include:
- Experimenting with pilot programs for new products
- Entering new market segments
- Building partnerships to leverage external innovations
Investments in Horizon 2 can facilitate smoother transitions into more transformative opportunities while reducing risk associated with market entry. This horizon often requires a culture of experimentation, where failure is seen as a stepping stone to success. Organizations may establish innovation labs or incubators to foster creativity and collaboration among teams. By actively seeking out strategic alliances and joint ventures, companies can tap into complementary strengths and share the burden of risk, ultimately accelerating their growth trajectory. Furthermore, understanding customer needs in emerging markets can provide valuable insights that guide product development and marketing strategies.
Horizon 3: Long-term Possibilities
Horizon 3 is all about envisioning the future. It encourages organizations to explore radical innovations or disruptive technologies that could redefine their business landscape. Although these opportunities may come with higher risk, they can also yield significant rewards. Strategic actions could involve:
- Research and development of breakthrough technologies
- Engaging with thought leaders and trendsetters
- Allocating resources to exploratory projects
A clear vision for Horizon 3 enables organizations to prepare for future changes in their industry, ensuring they are not merely reactive but rather proactive in their approach. This horizon often requires a long-term commitment to research and development, where organizations invest in understanding emerging trends and technologies that could disrupt their current business models. Engaging with futurists and industry experts can provide valuable foresight, allowing companies to anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and technological advancements. Moreover, fostering a culture that embraces change and encourages innovative thinking at all levels can empower employees to contribute ideas that may lead to groundbreaking developments, positioning the organization as a leader in its field.
Benefits of Implementing the McKinsey Three Horizons Model
The application of the McKinsey Three Horizons Model comes with several strategic advantages that can propel an organization to new heights. This section examines key benefits that businesses can gain through successful implementation.
Enhancing Business Growth
One of the primary advantages of the Three Horizons Model is its ability to foster growth. By diversifying focus across multiple horizons, organizations can ensure they are not overly reliant on a single revenue stream. This balanced approach can lead to:
- Increased resilience against market fluctuations
- Access to new revenue sources
- Enhanced ability to pivot based on market demands
Ultimately, this can lead to sustained long-term growth and stability for the organization. Furthermore, by identifying opportunities in both the near and distant future, companies can strategically allocate resources to initiatives that promise the highest potential return on investment. This proactive stance not only safeguards against economic downturns but also positions the organization as a leader in its industry, capable of adapting to changes and seizing new opportunities as they arise.
Facilitating Innovation
Innovation is essential for staying competitive, and the Three Horizons Model provides a structured framework to cultivate new ideas. By dedicating resources to emerging opportunities and long-term possibilities, organizations can:
- Encourage a culture of creativity and experimentation
- Support cross-functional collaboration
- Reduce the risk of stagnation in a rapidly evolving market
This emphasis on innovation not only helps in developing new offerings but also in refining existing ones. Moreover, by actively engaging employees at all levels in the innovation process, organizations can tap into a wealth of diverse perspectives and insights. This inclusivity not only boosts morale but also fosters a sense of ownership among staff, leading to higher levels of commitment and productivity. As a result, companies can create a dynamic environment where innovative ideas flourish and are translated into actionable strategies that drive growth.
Challenges in Applying the Three Horizons Model
Balancing the Three Horizons
One significant challenge is finding the right balance between the three horizons. Organizations often struggle to allocate resources effectively, as a predominant focus on Horizon 1 may lead to neglect of Horizons 2 and 3. To overcome this issue, businesses must:
- Establish clear metrics for measuring success across all horizons
- Engage leadership in strategic discussions about future investments
- Foster open communication channels across departments
Balancing these horizons allows organizations to remain agile and responsive to both current and future market demands.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Implementing the Three Horizons Model may also meet with resistance from within the organization. Employees accustomed to traditional methods might be hesitant to embrace a new framework. Effective strategies to mitigate this resistance include:
- Educating staff on the benefits of the model and its alignment with company goals
- Involving employees in the development of new initiatives to foster ownership
- Recognizing and reinforcing positive changes to encourage further adoption
By addressing resistance proactively, organizations can cultivate a culture open to growth and innovation.
Strategies for Effective Implementation of the Model
For organizations aiming to leverage the McKinsey Three Horizons Model effectively, specific strategies can facilitate a smoother implementation process. This section outlines essential steps to consider.
Aligning the Model with Business Goals
To ensure the model is effective, it should align seamlessly with the organization’s overall business objectives. This alignment requires:
- Regularly reviewing business goals and adjusting the model accordingly
- Engaging key stakeholders in discussions around strategy formulation
- Utilizing data-driven insights to guide decision-making processes
When the model is aligned with business goals, organizations are more likely to achieve their strategic vision.
Regular Review and Adjustment
Lastly, the dynamic nature of business requires that organizations continually assess the relevance of each horizon. Regular reviews and adjustments are crucial and can be accomplished through:
- Scheduling periodic strategy sessions to evaluate progress
- Soliciting feedback from team members and key stakeholders
- Utilizing performance metrics to track success over time
By proactively managing the Three Horizons Model, organizations can sustain their growth trajectory and remain competitive in an evolving landscape.
In summary, the McKinsey Three Horizons Model serves as a powerful strategic tool that can help businesses navigate the complexities of growth, innovation, and long-term sustainability. By understanding and effectively implementing the model, organizations can unlock new opportunities and ensure their position in an ever-changing market.